How to use Acceptable quality Level AQL
Selasa, 26 Juni 2018
Edit
ACCEPTABLE QUALITY LEVEL
is the "most tolerable" level of the average over
a period of batches. These tables are the United States standard equivalent in
all national and international standardization organizations (ANSI / ASQC Z1.4,
NF06-022, BS 6001, DIN 40080).
Basically, there are three types of defects that are often
differentiated. For most of its restricted goods or products are: Critical l% 0
defect for critical defects is totally unacceptable: users may be harmed, or
rules are not respected The major defect
of 2.5% for major defects of this product is usually not considered to be
acceptable to end-users The minor defect of 4.0% for small defects is some
departure from specs, but most users do not mind The Acceptable Quality Limit,
commonly referred to as an AQL, is a widely used method for measuring sample
production orders to find out whether all product orders have met the client's
specifications. Customers then have data to make informed decisions to accept
or reject them. Your Inspection Report will clearly state whether your
production has passed or failed on your preferred AQL. Note that this tool is
used most during the final outbound inspection when the product is ready to be
sent out and sometimes during production when the number of products is sufficient
to have an idea of the average quality AQL Tables the AQL table is the buyer
statistics tool (for product inspection). They are industry standards. Most of
the suppliers involved in international trade are already familiar with it AQL
/ acceptable quality level They help determine the two main elements:- How many
samples should be taken and checked, between a set of products or parts of the
quantity order?- Where is the limit
between acceptance and rejection, when it comes to defective products?
The need for objective quality measurement certain product
categories, there will be products that are handicapped almost every
production. Often true even after the manufacturer checks each individual
product and repairs the damaged, since the visual inspection is not 100%
reliable. Therefore, in many supplier / buyer relationships (especially when
the application does not produce live or dead), suppliers are not expected to
deliver flawed goods. The buyer needs to control the quality of the goods /
products purchased, because he does not want too much of the defective item How
to set a limit between acceptance and rejection in a way that can be agreed and
measured?
What the AQL (ACCEPTABLE QUALITY LEVEL) How to
determine the exact sample size and reception number? How to use the AQL table
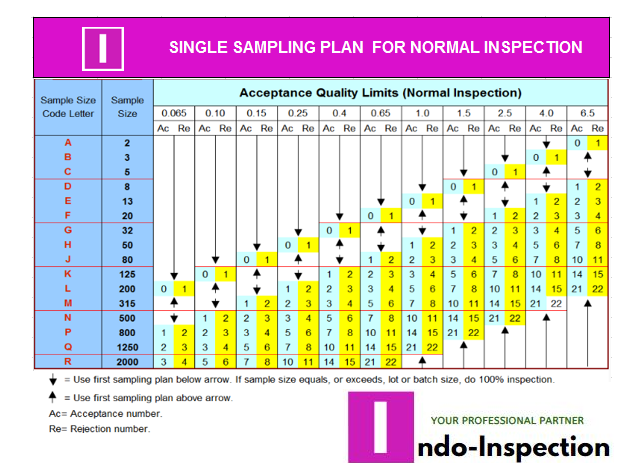
for correct checks for your needs. For production checks with 4,500 pcs with
Acceptable Quality Limit II, Table A shows the general inspection level
"L". Referring to Table B row L. For sample size 200, with AQL 2.5,
no more than 10 units may fail for forwarded reports
Using the AQL tables, importers should be aware of the
following three parameters:
The lot size – The number of items ordered is the lot size,
and it is advised to perform separate inspections for each lot. If only one
product was ordered, the lot size is the total batch quantity.
The inspection level – Three inspection levels dictate how many samples to inspect:
Level I – This is the least strict inspection level. It can
be used if the importer has a lower tolerance for product quality issues, such
as with lesser-value gifts that come free with a purchase. Or perhaps a
supplier has passed all previous inspections, and the buyer feels confident in
their product quality. It is important to understand that settling for a Level
I inspection as a way to spend less time and money is a high-risk strategy.
Level II – Used by default, Level II is the most widely
adopted.
Level III – The strictest inspection level, Level III
dictates the largest sample size and is, therefore, most representative of the
overall quality of the products. Buyers may opt for a Level III inspection for
high-value products (example: luxury goods)
You May Also Like:
- Step by Step Fabric Inspection
- The Top of Garments Visual Devect
- Soft-Lines and Hard-Line Inspection
- Type of Inspection
- Lashes Pre-shipment Inspection
- How to Rattan Chair processing
- How to Rattan Raw Matrial processing
- How to Know sintetic Rattan
- How to on Site Test of Toys
- How to Inspection Toys Electrics
- Toys Test Performed During Inspection
- Quality Control
- Quality Control Procedure
You May Also Like:
- Step by Step Fabric Inspection
- The Top of Garments Visual Devect
- Soft-Lines and Hard-Line Inspection
- Type of Inspection
- Lashes Pre-shipment Inspection
- How to Rattan Chair processing
- How to Rattan Raw Matrial processing
- How to Know sintetic Rattan
- How to on Site Test of Toys
- How to Inspection Toys Electrics
- Toys Test Performed During Inspection
- Quality Control
- Quality Control Procedure